Acetylene Gas
$0.00Pure Acetylene Gas
- Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution. Pure acetylene is odorless, but commercial grades usually have a marked odor due to impurities.
- As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because its two carbon atoms are bonded together in a triple bond. The carbon–carbon triple bond places all four atoms in the same straight line, with CCH bond angles of 180°. Since acetylene is a linear symmetrical molecule, it possesses the D∞h point group.
Acetylene Gas
$0.00Pure Acetylene Gas
- Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution. Pure acetylene is odorless, but commercial grades usually have a marked odor due to impurities.
- As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because its two carbon atoms are bonded together in a triple bond. The carbon–carbon triple bond places all four atoms in the same straight line, with CCH bond angles of 180°. Since acetylene is a linear symmetrical molecule, it possesses the D∞h point group.
Acetylene Gas
$0.00Pure Acetylene Gas
- Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution. Pure acetylene is odorless, but commercial grades usually have a marked odor due to impurities.
- As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because its two carbon atoms are bonded together in a triple bond. The carbon–carbon triple bond places all four atoms in the same straight line, with CCH bond angles of 180°. Since acetylene is a linear symmetrical molecule, it possesses the D∞h point group.
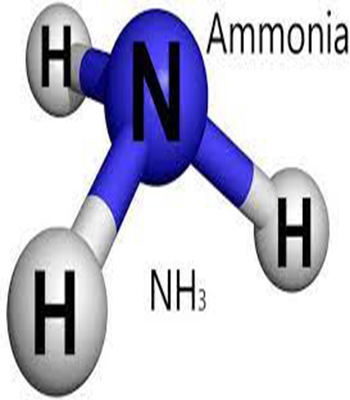
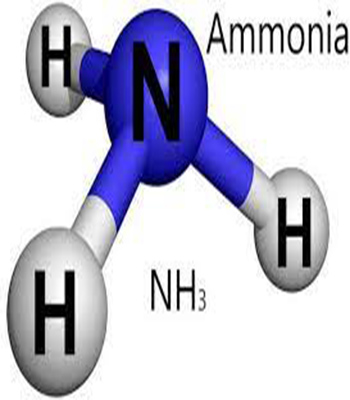
Ammonia Gas
$0.00Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula NH₃. A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct characteristic of a pungent smell
Ammonia Gas
$0.00Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula NH₃. A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct characteristic of a pungent smell
Ammonia Gas
$0.00Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula NH₃. A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct characteristic of a pungent smell
ARGON Gas
$0.00Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in the Earth’s atmosphere, at 0.934%.
Argon Gas
$0.00Argon is a chemical element with symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas.[3] Argon is the third most common gas in the Earth’s atmosphere, at 0.93% (9,300 ppm), making it approximately 23.8 times as abundant as the next most common atmospheric gas, carbon dioxide (390 ppm), and more than 500 times as abundant as the next most common noble gas, neon (18 ppm). Nearly all of this argon is radiogenic argon-40 derived from the decay of potassium-40 in the Earth’s crust. In the universe, argon-36 is by far the most common argon isotope, being the preferred argon isotope produced by stellar nucleosynthesis in supernovas.
ARGON Gas
$0.00Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in the Earth’s atmosphere, at 0.934%.
Argon Gas
$0.00Argon is a chemical element with symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas.[3] Argon is the third most common gas in the Earth’s atmosphere, at 0.93% (9,300 ppm), making it approximately 23.8 times as abundant as the next most common atmospheric gas, carbon dioxide (390 ppm), and more than 500 times as abundant as the next most common noble gas, neon (18 ppm). Nearly all of this argon is radiogenic argon-40 derived from the decay of potassium-40 in the Earth’s crust. In the universe, argon-36 is by far the most common argon isotope, being the preferred argon isotope produced by stellar nucleosynthesis in supernovas.
ARGON Gas
$0.00Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in the Earth’s atmosphere, at 0.934%.
Argon Gas
$0.00Argon is a chemical element with symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas.[3] Argon is the third most common gas in the Earth’s atmosphere, at 0.93% (9,300 ppm), making it approximately 23.8 times as abundant as the next most common atmospheric gas, carbon dioxide (390 ppm), and more than 500 times as abundant as the next most common noble gas, neon (18 ppm). Nearly all of this argon is radiogenic argon-40 derived from the decay of potassium-40 in the Earth’s crust. In the universe, argon-36 is by far the most common argon isotope, being the preferred argon isotope produced by stellar nucleosynthesis in supernovas.
Butane Specification
$0.00The product butane specifications are as follows:
| Capacity | 0.38 MTPA |
| Composition | |
|---|---|
| Butane Content | 95 liquid volume % (min.) |
| Pentane and heavier | 1.0 mole % (max.) |
| Quality | |
| Vapor pressure at 100 ºF | 70 psig (max.) |
| Volatile residue temp. at 95% evaporation | 36 ˚F (max.) |
| Corrosion, copper strip | No. 1 |
| Impurities | |
| Total sulfur | 0.001 wt % (max.) |
| Hydrogen Sulfide | negative |
Butane Specification
$0.00The product butane specifications are as follows:
| Capacity | 0.38 MTPA |
| Composition | |
|---|---|
| Butane Content | 95 liquid volume % (min.) |
| Pentane and heavier | 1.0 mole % (max.) |
| Quality | |
| Vapor pressure at 100 ºF | 70 psig (max.) |
| Volatile residue temp. at 95% evaporation | 36 ˚F (max.) |
| Corrosion, copper strip | No. 1 |
| Impurities | |
| Total sulfur | 0.001 wt % (max.) |
| Hydrogen Sulfide | negative |
Butane Specification
$0.00The product butane specifications are as follows:
| Capacity | 0.38 MTPA |
| Composition | |
|---|---|
| Butane Content | 95 liquid volume % (min.) |
| Pentane and heavier | 1.0 mole % (max.) |
| Quality | |
| Vapor pressure at 100 ºF | 70 psig (max.) |
| Volatile residue temp. at 95% evaporation | 36 ˚F (max.) |
| Corrosion, copper strip | No. 1 |
| Impurities | |
| Total sulfur | 0.001 wt % (max.) |
| Hydrogen Sulfide | negative |
Butterfly handle Gas Ball Valve
$0.00| Model : | Butterfly handle Gas Ball Valve |
| Company name : | Iran Gas Valve |
| Packaging : | – |
| Minimum order : | 1 |
| Standard : | – |
| Production power : | – |
Butterfly handle Gas Ball Valve
$0.00| Model : | Butterfly handle Gas Ball Valve |
| Company name : | Iran Gas Valve |
| Packaging : | – |
| Minimum order : | 1 |
| Standard : | – |
| Production power : | – |
Butterfly handle Gas Ball Valve
$0.00| Model : | Butterfly handle Gas Ball Valve |
| Company name : | Iran Gas Valve |
| Packaging : | – |
| Minimum order : | 1 |
| Standard : | – |
| Production power : | – |
Carbon dioxide Gas
$0.00Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a nonflammable, colorless, odorless gas. It is found in air at concentration of about 0.03%. Carbon dioxide may exist simultaneously as a solid, liquid, and gas at a temperature of -56.6˚C and a pressure of 60.4 psig. At a temperature of -79˚C and atmospheric pressure, carbon dioxide solidifies forming “dry ice” at density of 97.4 pounds per cubic foot. Because of its low concentration in the atmosphere, air is not a suitable feedstock for carbon dioxide production. Rather, CO2 is obtained from by-product streams from various manufacturing processes. Bulk quantities of carbon dioxide are usually stored and shipped as liquid under elevated pressure and refrigeration.
Blanketing and purging of tanks and reactors. It is also used as shielding gas in the arc welding process. It is the source of the bubbles in soft drinks and other carbonated beverages. It is used to fill certain types of fire extinguishers that rely on its inert properties, densities, and low temperature when released from high-pressure storage.In addition to its “inert” properties, carbon dioxide, as dry ice, is used to freeze a variety of foods.
Carbon dioxide Gas
$0.00Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a nonflammable, colorless, odorless gas. It is found in air at concentration of about 0.03%. Carbon dioxide may exist simultaneously as a solid, liquid, and gas at a temperature of -56.6˚C and a pressure of 60.4 psig. At a temperature of -79˚C and atmospheric pressure, carbon dioxide solidifies forming “dry ice” at density of 97.4 pounds per cubic foot. Because of its low concentration in the atmosphere, air is not a suitable feedstock for carbon dioxide production. Rather, CO2 is obtained from by-product streams from various manufacturing processes. Bulk quantities of carbon dioxide are usually stored and shipped as liquid under elevated pressure and refrigeration.
Blanketing and purging of tanks and reactors. It is also used as shielding gas in the arc welding process. It is the source of the bubbles in soft drinks and other carbonated beverages. It is used to fill certain types of fire extinguishers that rely on its inert properties, densities, and low temperature when released from high-pressure storage.In addition to its “inert” properties, carbon dioxide, as dry ice, is used to freeze a variety of foods.
Carbon dioxide Gas
$0.00Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a nonflammable, colorless, odorless gas. It is found in air at concentration of about 0.03%. Carbon dioxide may exist simultaneously as a solid, liquid, and gas at a temperature of -56.6˚C and a pressure of 60.4 psig. At a temperature of -79˚C and atmospheric pressure, carbon dioxide solidifies forming “dry ice” at density of 97.4 pounds per cubic foot. Because of its low concentration in the atmosphere, air is not a suitable feedstock for carbon dioxide production. Rather, CO2 is obtained from by-product streams from various manufacturing processes. Bulk quantities of carbon dioxide are usually stored and shipped as liquid under elevated pressure and refrigeration.
Blanketing and purging of tanks and reactors. It is also used as shielding gas in the arc welding process. It is the source of the bubbles in soft drinks and other carbonated beverages. It is used to fill certain types of fire extinguishers that rely on its inert properties, densities, and low temperature when released from high-pressure storage.In addition to its “inert” properties, carbon dioxide, as dry ice, is used to freeze a variety of foods.
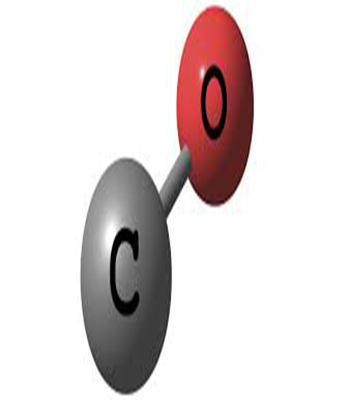
Carbon monoxide (CO) Gas
$0.00Carbon monoxide (CO) gas is formed from the combination of a carbon atom with an oxygen atom. Not only flammable, it is also very hazardous since it is very toxic and odorless. It cannot sustain life and is produced, among other things, from incomplete combustion due to lack of oxygen. It can therefore cause domestic accidents if heating systems are poorly maintained. It is produced on a large scale in industry, in combination with hydrogen, by reforming hydrocarbons, generally natural gas. It is used in large quantities to produce various intermediary organic chemicals, such as acetic acids, isocyanates, formic acid, and also certain polymers such as polycarbonates and polyketones.
Carbon monoxide (CO) Gas
$0.00Carbon monoxide (CO) gas is formed from the combination of a carbon atom with an oxygen atom. Not only flammable, it is also very hazardous since it is very toxic and odorless. It cannot sustain life and is produced, among other things, from incomplete combustion due to lack of oxygen. It can therefore cause domestic accidents if heating systems are poorly maintained. It is produced on a large scale in industry, in combination with hydrogen, by reforming hydrocarbons, generally natural gas. It is used in large quantities to produce various intermediary organic chemicals, such as acetic acids, isocyanates, formic acid, and also certain polymers such as polycarbonates and polyketones.
Carbon monoxide (CO) Gas
$0.00Carbon monoxide (CO) gas is formed from the combination of a carbon atom with an oxygen atom. Not only flammable, it is also very hazardous since it is very toxic and odorless. It cannot sustain life and is produced, among other things, from incomplete combustion due to lack of oxygen. It can therefore cause domestic accidents if heating systems are poorly maintained. It is produced on a large scale in industry, in combination with hydrogen, by reforming hydrocarbons, generally natural gas. It is used in large quantities to produce various intermediary organic chemicals, such as acetic acids, isocyanates, formic acid, and also certain polymers such as polycarbonates and polyketones.
Carbon Monoxide Gas
$0.00The Co unit production capacity is 140 kt/y of Carbon Monoxide,the feed of which is natural gas received from the National Iranian Gas Company at the rate of 87927 T/Y. The feed is mixed with steam after desulphurization and flow through the pre reformer at which higher hydrocarbons are broken to methane,CO,CO2 and Hydrogen and then passes through the reformer where sysngas is formed from the endothermic reaction of methane with steam .The reformer outlet steam is cooled to condensate and separate water ,then its CO2 content is separated by amine solution and returned to the reformer and discharged H2&CO are separated in a cold box to produce pure carbon monoxide product.
Carbon Monoxide Gas
$0.00The Co unit production capacity is 140 kt/y of Carbon Monoxide,the feed of which is natural gas received from the National Iranian Gas Company at the rate of 87927 T/Y. The feed is mixed with steam after desulphurization and flow through the pre reformer at which higher hydrocarbons are broken to methane,CO,CO2 and Hydrogen and then passes through the reformer where sysngas is formed from the endothermic reaction of methane with steam .The reformer outlet steam is cooled to condensate and separate water ,then its CO2 content is separated by amine solution and returned to the reformer and discharged H2&CO are separated in a cold box to produce pure carbon monoxide product.
Carbon Monoxide Gas
$0.00The Co unit production capacity is 140 kt/y of Carbon Monoxide,the feed of which is natural gas received from the National Iranian Gas Company at the rate of 87927 T/Y. The feed is mixed with steam after desulphurization and flow through the pre reformer at which higher hydrocarbons are broken to methane,CO,CO2 and Hydrogen and then passes through the reformer where sysngas is formed from the endothermic reaction of methane with steam .The reformer outlet steam is cooled to condensate and separate water ,then its CO2 content is separated by amine solution and returned to the reformer and discharged H2&CO are separated in a cold box to produce pure carbon monoxide product.
Condensate-Natural Gas Condensate
$0.00The natural gas condensate is also called condensate, or gas condensate, or sometimes natural gasoline because it contains hydrocarbons within the gasoline boiling range, and is also referred to by the shortened name condy by many workers on gas installations.In general, gas condensate has a specific gravity ranging from 0.5 to 0.8, and is composed of hydrocarbons such as propane, butane, pentane, and hexane. Natural gas compounds with more than two carbon atoms exist as liquids at ambient temperatures
Condensate-Natural Gas Condensate
$0.00Gas condensate is mostly composed of pentane and heavier hydrocarbons (+ C5) and depending on its harvesting position can contain sulfur and salt and is usually free of metals and about half of it is naphtha.
Unlike butane and propane, gas condensates do not require special conditions to remain liquid and can be converted to diesel, gasoline, kerosene, jet fuel, etc. in various ways. Compared to crude oil refinery, in gas condensate refinery, conversion and refining processes are less, so its investment cost is less than the investment cost of crude oil refinery.
The specific calorific value of each liter of gas condensate is about 32706 BTU, which is approximately equal to the heat value of 826 /. Cubic meters of natural gas is the first national pipeline; Therefore, this product is of considerable importance for export due to its high calorific value. In such a way that its export can return the initial investment cost of a gas refinery in a short period of time, provided that it has the desired technical characteristics.
Condensate-Natural Gas Condensate
$0.00Gas condensate is mostly composed of pentane and heavier hydrocarbons (+ C5) and depending on its harvesting position can contain sulfur and salt and is usually free of metals and about half of it is naphtha.
Unlike butane and propane, gas condensates do not require special conditions to remain liquid and can be converted to diesel, gasoline, kerosene, jet fuel, etc. in various ways. Compared to crude oil refinery, in gas condensate refinery, conversion and refining processes are less, so its investment cost is less than the investment cost of crude oil refinery.
The specific calorific value of each liter of gas condensate is about 32706 BTU, which is approximately equal to the heat value of 826 /. Cubic meters of natural gas is the first national pipeline; Therefore, this product is of considerable importance for export due to its high calorific value. In such a way that its export can return the initial investment cost of a gas refinery in a short period of time, provided that it has the desired technical characteristics.
Condensate-Natural Gas Condensate
$0.00Gas condensate is mostly composed of pentane and heavier hydrocarbons (+ C5) and depending on its harvesting position can contain sulfur and salt and is usually free of metals and about half of it is naphtha.
Unlike butane and propane, gas condensates do not require special conditions to remain liquid and can be converted to diesel, gasoline, kerosene, jet fuel, etc. in various ways. Compared to crude oil refinery, in gas condensate refinery, conversion and refining processes are less, so its investment cost is less than the investment cost of crude oil refinery.
The specific calorific value of each liter of gas condensate is about 32706 BTU, which is approximately equal to the heat value of 826 /. Cubic meters of natural gas is the first national pipeline; Therefore, this product is of considerable importance for export due to its high calorific value. In such a way that its export can return the initial investment cost of a gas refinery in a short period of time, provided that it has the desired technical characteristics.
Condensate-Natural Gas Condensate
$0.00The natural gas condensate is also called condensate, or gas condensate, or sometimes natural gasoline because it contains hydrocarbons within the gasoline boiling range, and is also referred to by the shortened name condy by many workers on gas installations.In general, gas condensate has a specific gravity ranging from 0.5 to 0.8, and is composed of hydrocarbons such as propane, butane, pentane, and hexane. Natural gas compounds with more than two carbon atoms exist as liquids at ambient temperatures
Condensate-Natural Gas Condensate
$0.00The natural gas condensate is also called condensate, or gas condensate, or sometimes natural gasoline because it contains hydrocarbons within the gasoline boiling range, and is also referred to by the shortened name condy by many workers on gas installations.In general, gas condensate has a specific gravity ranging from 0.5 to 0.8, and is composed of hydrocarbons such as propane, butane, pentane, and hexane. Natural gas compounds with more than two carbon atoms exist as liquids at ambient temperatures
Ethylene Gas
$0.00Ethylene (IUPAC name: Ethene) is a hydrocarbon with the formula C2H4 or H2C=CH2. It is a colorless flammable gas with a faint “sweet and musky” odor when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds), and the second simplest unsaturated hydrocarbon after acetylene (C2H2). Ethylene is widely used in chemical industry, and its worldwide production (over 109 million tonnes in 2006) exceeds that of any other organic compound. Ethylene is also an important natural plant hormone, used in agriculture to force the ripening of fruits Global ethylene production was 107 million tonnes in 2005 … .
Ethylene Gas
$0.00Ethylene (IUPAC name: Ethene) is a hydrocarbon with the formula C2H4 or H2C=CH2. It is a colorless flammable gas with a faint “sweet and musky” odor when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds), and the second simplest unsaturated hydrocarbon after acetylene (C2H2). Ethylene is widely used in chemical industry, and its worldwide production (over 109 million tonnes in 2006) exceeds that of any other organic compound. Ethylene is also an important natural plant hormone, used in agriculture to force the ripening of fruits Global ethylene production was 107 million tonnes in 2005 … .
Ethylene Gas
$0.00Ethylene (IUPAC name: Ethene) is a hydrocarbon with the formula C2H4 or H2C=CH2. It is a colorless flammable gas with a faint “sweet and musky” odor when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds), and the second simplest unsaturated hydrocarbon after acetylene (C2H2). Ethylene is widely used in chemical industry, and its worldwide production (over 109 million tonnes in 2006) exceeds that of any other organic compound. Ethylene is also an important natural plant hormone, used in agriculture to force the ripening of fruits Global ethylene production was 107 million tonnes in 2005 … .